近半年来,新冠肺炎席卷全球且目前还处于大流行的状态,临床上急需基于胸部CT的COVID-19自动筛查系统。医学人工智能研究中心主任魏本征教授带领团队与山东省中医院肺病科主任张伟教授通力合作,充分发挥本中心在人工智能上的技术优势,并结合新冠肺炎胸部影像学特点研究出了一种基于注意力的深度3D多示例学习方法(AD3D-MIL)来实现COVID-19的自动筛查。研究结果表明,该方法可实现97.9%的总体筛查准确度、99.0%的AUC和95.7%的Cohen kappa得分,是一种影像学筛查COVID-19的潜在有效辅助工具。研究论文“Accurate Screening of COVID-19 using Attention Based Deep 3D Multiple Instance Learning”,已由医学成像领域期刊IEEE Transactions on Medical Imaging(IF=6.685)优先在线发表。(论文链接地址:https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/9098062)
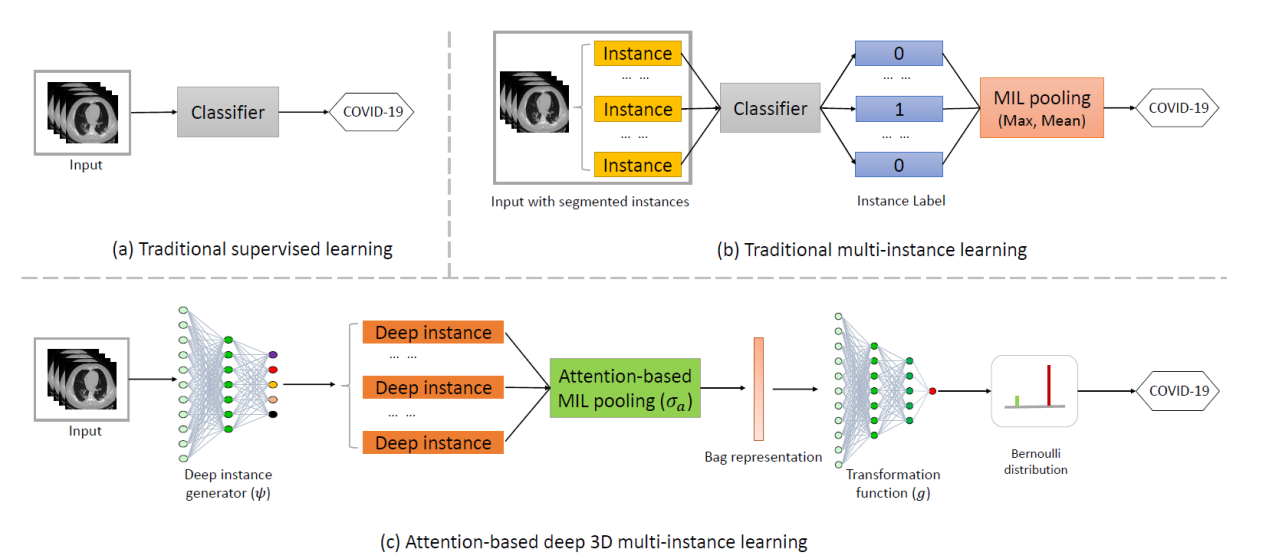
论文摘要:自2020年全球SARS-CoV-2病毒爆发以来,临床上急需基于胸部CT的COVID-19自动筛查系统。但是,由于3D体积的空间复杂性、感染区域标记的困难性,以及COVID-19与其他病毒性肺炎在胸部CT上的特征差异较小,准确筛查COVID-19仍然是一项巨大的挑战。尽管一些开创性工作已经取得了一些进展,但他们需要感染区域的人工标注,并缺乏解释性。在本文中,我们旨在只使用弱标签的胸部CT数据实现对COVID-19的高精度和可解释性筛查。我们提出了一种基于注意力的深度3D多示例学习方法(AD3D-MIL),将患者级别的标签分配给3D胸部CT,并将此CT视为示例包(a bag of instances)。AD3D-MIL可以生成具有语义信息的深层3D示例,每个示例可能对应着潜在的感染区域。AD3D-MIL还将基于注意力的池化方法应用于深度3D示例,以挖掘每个示例对最终分类结果的贡献度。 AD3D-MIL最终学习了示例包的伯努利分布以更轻松地实现筛查。我们收集了460例胸部CT数据:包括79例COVID-19患者的230例CT,100例普通肺炎患者的100例CT和130例非肺炎的130例CT。一系列实验研究表明,我们的算法实现了97.9%的总体筛查准确度,99.0%的AUC和95.7%的Cohen kappa得分。这些优点使我们的算法可成为基于影像学辅助筛查COVID-19的潜在工具。
Abstract:Automated Screening of COVID-19 from chest CT is of emergency and importance during the outbreak of SARS-CoV-2 worldwide in 2020. However, accurate screening of COVID-19 is still a massive challenge due to the spatial complexity of 3D volumes, the labeling difficulty of infection areas, and the slight discrepancy between COVID-19 and other viral pneumonia in chest CT. While a few pioneering works have made significant progress, they are either demanding manual annotations of infection areas or lack of interpretability. In this paper, we report our attempt towards achieving highly accurate and interpretable screening of COVID-19 from chest CT with weak labels. We propose an attention-based deep 3D multiple instance learning (AD3D-MIL) where a patient-level label is assigned to a 3D chest CT that is viewed as a bag of instances. AD3D-MIL can semantically generate deep 3D instances following the possible infection area. AD3D-MIL further applies an attention-based pooling approach to 3D instances to provide insight into each instance’s contribution to the bag label. AD3D-MIL finally learns Bernoulli distributions of the bag-level labels for more accessible learning. We collected 460 chest CT examples: 230 CT examples from 79 patients with COVID-19, 100 CT examples from 100 patients with common pneumonia, and 130 CT examples from 130 people without pneumonia. A series of empirical studies show that our algorithm achieves an overall accuracy of 97.9%, AUC of 99.0%, and Cohen kappa score of 95.7%. These advantages endow our algorithm as an efficient assisted tool in the screening of COVID-19.