研究中心硕士生袁航的一篇论文“MPANet: Multi-scale Pyramid Attention Network for Collaborative Modeling Spatio-Temporal Patterns of Default Mode Network”被AI 2023: Advances in Artificial Intelligence选为大会oral论文并收录。(论文链接地址:https://link.springer.com/chapter/10.1007/978-981-99-8388-9_34)
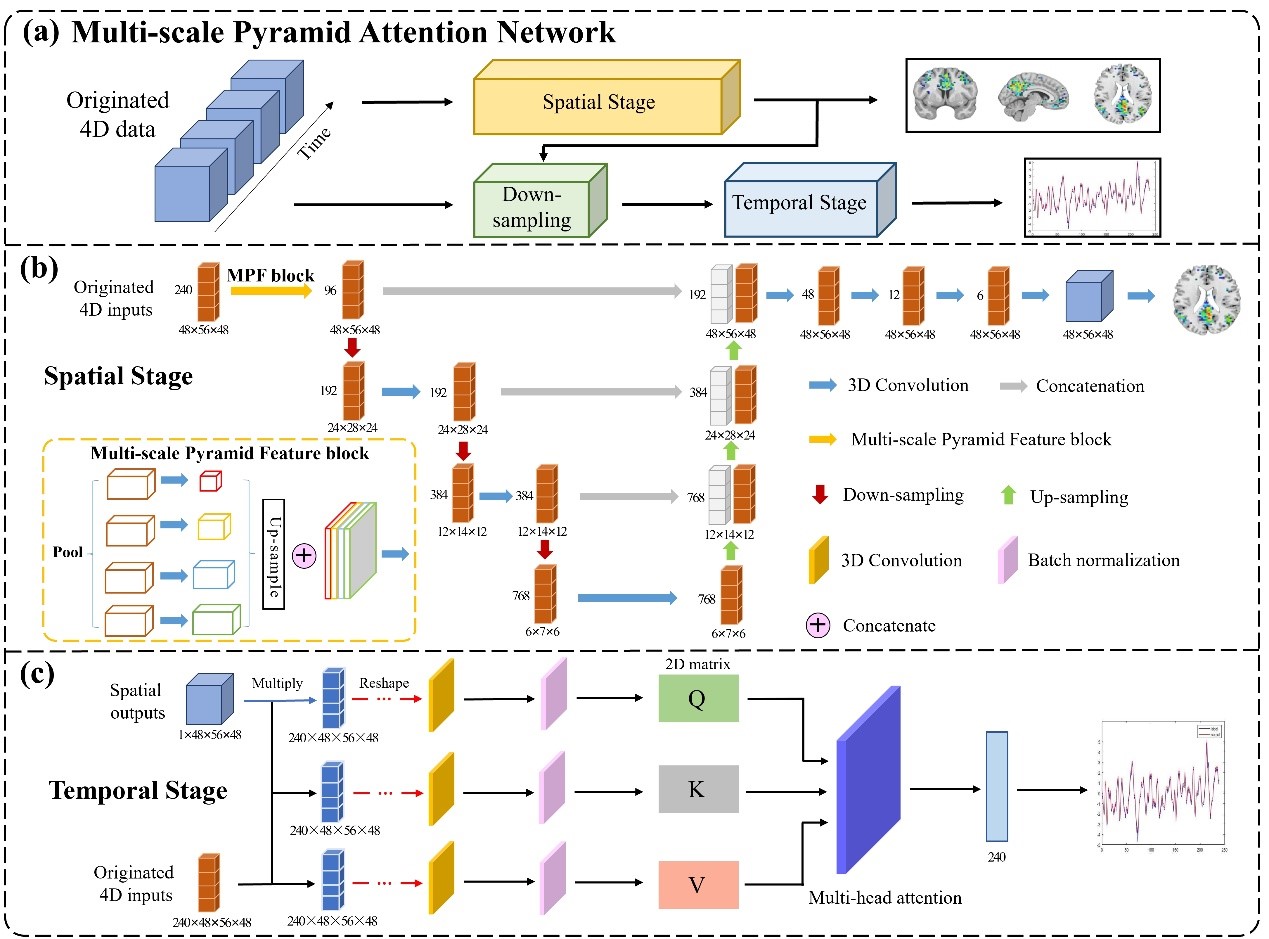
论文摘要: 静息状态下默认模式网络(DMN)的功能活动是复杂而自发的。基于四维静息态功能磁共振成像(Rs-fMRI)的默认模式网络时空模式建模为探索自发的大脑功能活动提供了基础。然而,如何在模型的浅层阶段利用时空特征完成对具有不同特征的四维Rs-fMRI的多层次刻画,准确表征DMN整体时空模式,仍然是当前DMN时空模式建模的挑战。为此,我们提出了多尺度金字塔注意网络(MPANet)以关注模型浅层特征,建模静息态个性化DMN时空模式。具体来说,在空间阶段,我们在浅层设计了一个多尺度金字塔区块,以扩大感受野并提取不同层次的细节信息,从而实现特征增强并引导模型表征DMN空间模式。在时间阶段,通过快速下采样操作和引入多头注意块,实现了从空间到时间模式的并行引导,从而更有效地融合时空特征。基于公开数据集的结果表明,MPANet 优于其他先进方法。该网络为个体DMN时空模式建模提供了一种强大的工具,其卓越的性能表明它在临床应用方面具有广阔的前景。
Abstract: The functional activity of the default mode network (DMN) in the resting state is complex and spontaneous. Modeling spatiotemporal patterns of DMN based on four-dimensional Resting-state functional Magnetic Resonance Imaging (Rs-fMRI) provides a basis for exploring spontaneous brain functional activities. However, how to utilize spatio-temporal features to complete the multi-level description of 4D Rs-fMRI with diverse characteristics in the shallow stage of the model and accurately characterize the DMN holistic spatio-temporal patterns remains challenging in the current DMN spatio-temporal patterns modeling. To this end, we propose a Multi-scale Pyramid Attention Network (MPANet) to focus on shallow features and model the spatio-temporal patterns of resting-state personalized DMN. Specifically, in the spatial stage, we design a multi-scale pyramid block in the shallow layer to expand the receptive field and extract granular information at different levels, which realize feature enhancement and guides the model to characterize the DMN spatial pattern. In the temporal stage, parallel guidance from spatial to the temporal pattern is achieved through the fast down-sampling operation and introduction of multi-head attention blocks for a more effective fusion of spatio-temporal features. The results based on a publicly available dataset demonstrate that MPANet outperforms other state-of-the-art methods. This network presents a robust tool for modeling the spatio-temporal patterns of individuals with DMN, and its exceptional performance suggests promising potential for clinical applications.