近日,研究中心博士生李翔的一篇论文“MH2AFormer: An Efficient Multiscale Hierarchical Hybrid Attention with a Transformer for Bladder Wall and Tumor Segmentation”被IEEE Journal of Biomedical and Health Informatics(JCR一区,影响因子7.7)录用。(论文链接地址: https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/10521702)
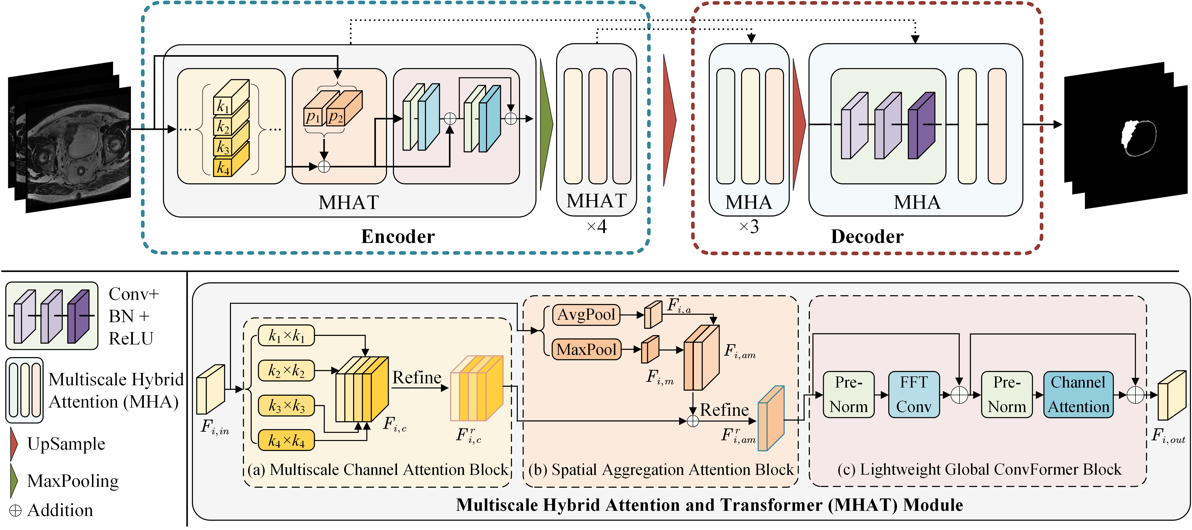
论文摘要:从MRI图像中准确分割膀胱壁和肿瘤区域对于临床诊断和治疗膀胱癌症至关重要。然而,由于器官间相似的密度分布、复杂的肿瘤形态和不清晰的边界等因素,自动分割仍然具有挑战性。考虑到膀胱MRI图像的特性,本文提出了一种有效的肿瘤和膀胱壁分割算法(MH2AFormer)。具体而言,本文在编码阶段设计了多尺度混合注意力和Transformer(MHAT)模块,用于从输入图像中自适应地提取和聚合多尺度混合特征表示。在解码器阶段,本文设计了一个多尺度混合注意力(MHA)模块,从多尺度混合特征中生成高质量的分割结果。上述模块的组合增强了特征表示,并引导模型关注肿瘤和膀胱壁壁区域,这有助于解决膀胱图像分割的挑战。此外,MHAT模块利用具有大内核(例如,224 224)的快速傅立叶变换来对全局特征关系进行建模,同时降低编码阶段的计算复杂度。本文在两个数据集上评估了模型性能,均取得了最佳的结果(数据集A: IoU=80.26%,DSC=88.20%;数据集B: IoU=89.74%,DSC=94.48%)。上述实验结果证实了本文方法的实用性,突出了其在临床应用时减轻放射科医生工作量的潜力。
224)的快速傅立叶变换来对全局特征关系进行建模,同时降低编码阶段的计算复杂度。本文在两个数据集上评估了模型性能,均取得了最佳的结果(数据集A: IoU=80.26%,DSC=88.20%;数据集B: IoU=89.74%,DSC=94.48%)。上述实验结果证实了本文方法的实用性,突出了其在临床应用时减轻放射科医生工作量的潜力。
Abstract: Achieving accurate bladder wall and tumor segmentation from MRI is critical for diagnosing and treating bladder cancer. However, automated segmentation remains challenging due to factors such as comparable density distributions, intricate tumor morphologies, and unclear boundaries. Considering the attributes of bladder MRI images, we propose an efficient multiscale hierarchical hybrid attention with a transformer (MH2AFormer) for bladder cancer and wall segmentation. Specifically, a multiscale hybrid attention and transformer (MHAT) module in the encoder is designed to adaptively extract and aggregate multiscale hybrid feature representations from the input image. In the decoder stage, we devise a multiscale hybrid attention (MHA) module to generate high-quality segmentation results from multiscale hybrid features. Combining these modules enhances the feature representation and guides the model to focus on tumor and wall regions, which helps to solve bladder image segmentation challenges. Moreover, MHAT utilizes the Fast Fourier Transformer with a large kernel (e.g., 224 224) to model global feature relationships while reducing computational complexity in the encoding stage. The model performance was evaluated on two datasets. As a result, the model achieves relatively best results regarding the intersection over union (IoU) and dice similarity coefficient (DSC) on both datasets (Dataset A: IoU=80.26%, DSC=88.20%; Dataset B: IoU=89.74%, DSC=94.48%). These advantageous outcomes substantiate the practical utility of our approach, highlighting its potential to alleviate the workload of radiologists when applied in clinical settings.
224) to model global feature relationships while reducing computational complexity in the encoding stage. The model performance was evaluated on two datasets. As a result, the model achieves relatively best results regarding the intersection over union (IoU) and dice similarity coefficient (DSC) on both datasets (Dataset A: IoU=80.26%, DSC=88.20%; Dataset B: IoU=89.74%, DSC=94.48%). These advantageous outcomes substantiate the practical utility of our approach, highlighting its potential to alleviate the workload of radiologists when applied in clinical settings.